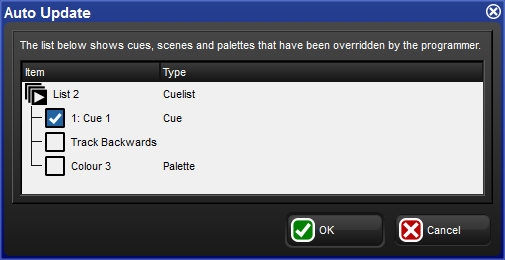
When you are programming a complex show, the look on stage may be built up from cuelists and scenes on several masters. You can change the look by assigning fixture parameter values in the Programmer, but it is difficult to know which cue or scene is contributing which values to the total on stage. Hog 4 OS's Auto Update feature automatically suggests the appropriate cues, palettes and scenes to merge the changes into, allowing you to choose how the updates are performed.
When you have finished editing in the Programmer you can merge the parameter values into the currently playing cues, palettes and scenes by pressing the Update key. The Auto Update window will open, showing which cuelists, cues, palettes and scenes are contributing to the look on stage so that you can choose which to update
For cuelists, you have several choices:
Either update the current cue in the cuelist, or track the programming backwards so that the new values are merged into the last cue with a hard value for that parameter; see Tracking Values Backwards When Recording.
If you have existing programming that refers to a palette, you can choose to update the palette instead of adding new parameter values to a cue. In this case, these updates will be performed first, and anything left in the Programmer after this will be used to update the selected cue or Track Backwards.
For scenes, you have the option to merge the programming into the scene, or into the palettes that are referred to in that scene.
Once you have chosen your options, press OK to perform the update. Note that the parameter values remain in the Programmer.
![[Tip]](../images/tip.png) | Tip |
|---|---|
If there is no playback on stage when you press Update, the Auto Update window will not appear and the Update key press is ignored. |
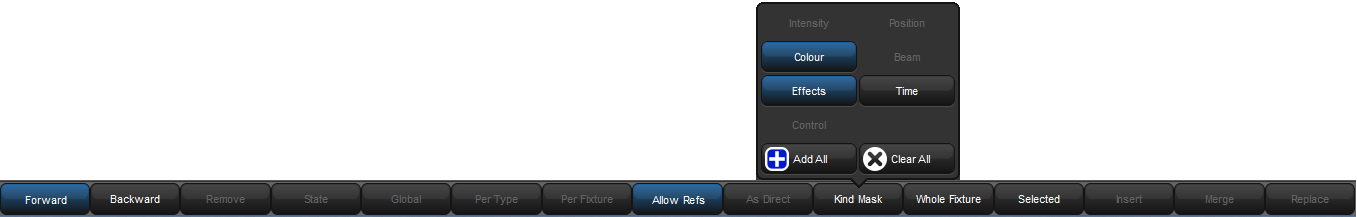
When you press the Update key, the Update Toolbar will also appear; see Figure 16.2, “The Update Toolbar”. This allows you to select which parameter types are updated, whether changes should track forwards, and whether references should be allowed when updating palettes. See Recording Palettes with Kind Masking, Stopping Values from Tracking Forward and Reference Palettes.